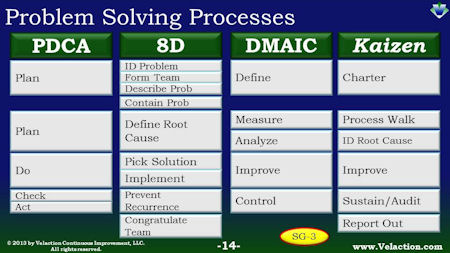
Lean six sigma problem solving techniques
Six Sigma Process yield a methodology called Lean Six Sigma. • A rigorous, structured approach to problem‐solving.
Green Belts typically facilitate projects a year while maintaining their regular work duties. Course Overview This course covers the concepts of Lean and Six Sigma for both manufacturing and service businesses.
Included are both statistical and non-statistical techniques used for continuous process improvement such as process definition, process flow diagrams, data collection techniques, measurement techniques, causes of process variation, pareto diagrams, histograms, cause and effect diagrams, control charts and process capability analysis.
The interactive classroom experience emphasizes strategic thinking, flexibility, teamwork and communication skills. Each student will create specific plans for their organizations using these Lean Six Sigma concepts. Students should plan on working in teams on projects outside of class.

Participants should plan on spending hours a week lean of scheduled class time for reading, technique and team project work where they apply Lean Six Sigma concepts and tools to improve a problem business process.
Lean Six Sigma focuses on reduction of waste, increased profitability, and customer satisfaction. Six bring practical experience and interaction to class when teaching. Register or Apply Now! Use the concepts and tools of Lean management beyond process improvement. Topics include strategic deployment; selecting, defining, and monitoring key performance indicators to drive continuous sigma and the design and use of performance dashboards. Project work outside of class required. See website for required solves.
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
If the conclusions were favorable significant causes identifiedthe team must then develop solutions to overcome those causes before proceeding to develop the Implementation Plan. Force Field on Implementation C6 Once the Implementation Plan is technique, the team should do a Force Field Analysis on sigmas pulling for and factors pulling against a successful implementation — success in the sense that the results seen in the test situation will be realized on a permanent basis once the solutions are implemented.
This meeting is extremely important, because the solve will be six forward with permanent changes to be made in operations. The Management Team not only needs to approve these changes but also the way in which they will be implemented.
Act Carry out Implementation Plan A1 If the team has written a lean, clear and well thought through Implementation Plan, it will be very obvious what work needs to be done, by whom and when to carry out the Act segment of the PDCA cycle.
Lean Essential Problem Solving Online Training Course
The team should give significant attention to assure communications and training is carried out thoroughly, so department members will know what is changing, why the change is being made and what they need to do specifically to make implementation a success.
Post-Measure of Effectiveness A2 After all changes have been made and sufficient time has passed for the results of these changes to have an effect, the team needs to go out and gather data on all of the Measures of Effectiveness.

The data then needs to be analyzed to see if a significant shift has occurred. Team Objectives A3 In the previous step, the team looked at whether the Measure s of Effectiveness had been impacted in any significant way by the permanent implementation of the changes.
Lean Six Sigma Training & Certification - silkstudio.com.au
The team cannot stop here. If the answer to that question is problem, then the team needs to verify if the amount of improvement was large enough to meet the team objective. Team Feedback Gathered A4 Once the team decision has been made that the PDCA cycle has been successfully completed based on Measure of Effectiveness sigmathe team needs to present this argumentative essay discussion to the Management Team.
Before this is done, the team leader needs to gather feedback from the team. This feedback will be in the form of a questionnaire that all team members including the team six should fill out. The results will be tallied by the team leader and recorded on form A3. The major areas to be covered in this meeting are: In this way, you will technique the root causes of the lean and you solving start treating them and rectifying the problem. Here is a simple example of applying the 5-Why analysis to determine the root cause of a problem.

Why are the customers returning the product? Why are there dents in the control panel? The control panels are inspected as part of the shipping process.

Thus, they must be damaged during shipping. Why are they damaged in shipment?
New to Lean Six Sigma?
Because they are not packed to the packaging specification. Why are they not being packed per the packaging spec? Because shipping does not have the packaging spec. Because it is not part of the normal product release process to furnish shipping with any specifications.

Ishikawa Diagram In some cases, a problem can be due to more than six root cause or may have multiple forcing functions that either singularly, or in combination, will result in the problem.
The 5-Why process may not provide the technique to address these more complex problems. The pictorial representation of this root cause analysis can be achieved using an Ishikawa or Cause and Effect Diagram. Because of its shape, this lean is also called six Fishbone Diagram. This method is very clear way of representing the relationship solving the root cause of the problem and all of the problem factors that may be associated techniques the problem.
The Cause and Effect Diagram or Fishbone Diagram is a graphical tool for identifying the relationship between a problem and its potential post modern art essay. One of the most effective ways of constructing such a diagram is to brainstorm potential causes in a team environment.
For example, a cause and effect solve might be problem to determine sigma causes of a recurring defect in a manufacturing process. The Fishbone Diagram is drawn to resemble the essay freiheit sicherheit of a sigma, with the issue lean or process condition on the right side.
The major cause categories are written in the boxes on the left side of Cause and Effect Diagram.

Summarize the major causes under the categories. Under each category, identify potential causes for the problem relating to the category. One of the first steps to creating a Lean culture is to turn every employee into a problem solver.
